Mitotic anaphase differs from the anaphase I of meiosis because Option Biology Diagrams Motor proteins generate forces that drive chromatid movement. Dynein moves toward the minus end of microtubules, pulling chromatids toward spindle poles. Kinesin-13 facilitates microtubule disassembly at kinetochores and spindle poles, aiding chromatid movement. In Anaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs separate, reducing chromosome number

ADVERTISEMENTS: Read this article to learn about the Movement of Chromosomes during Anaphase ! During nuclear division or mitosis, there is a progressive change in the structure and appearance of the chromosomes. Although mitosis is a continuous process (Figs. 20-20 and 20-21), for convenience it is usually divided into four major stages: prophase, meta- phase, […] Anaphase Spindle Generates More Force than Needed for Anaphase Chromosome Movement. It might seem natural to assume that the spindle forces normally generated during anaphase, when the chromosomes are undergoing their most obvious movements, are higher than during other phases of mitosis. In anaphase I, homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite ends of the cell. This ensures that each resulting daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. What Is Anaphase 1 Vs Anaphase 2? Anaphase 1 separates homologous chromosomes, Anaphase 2 separates sister chromatids. Both involve chromosome movement to opposite poles.
Definition, Process and Quiz Biology Diagrams
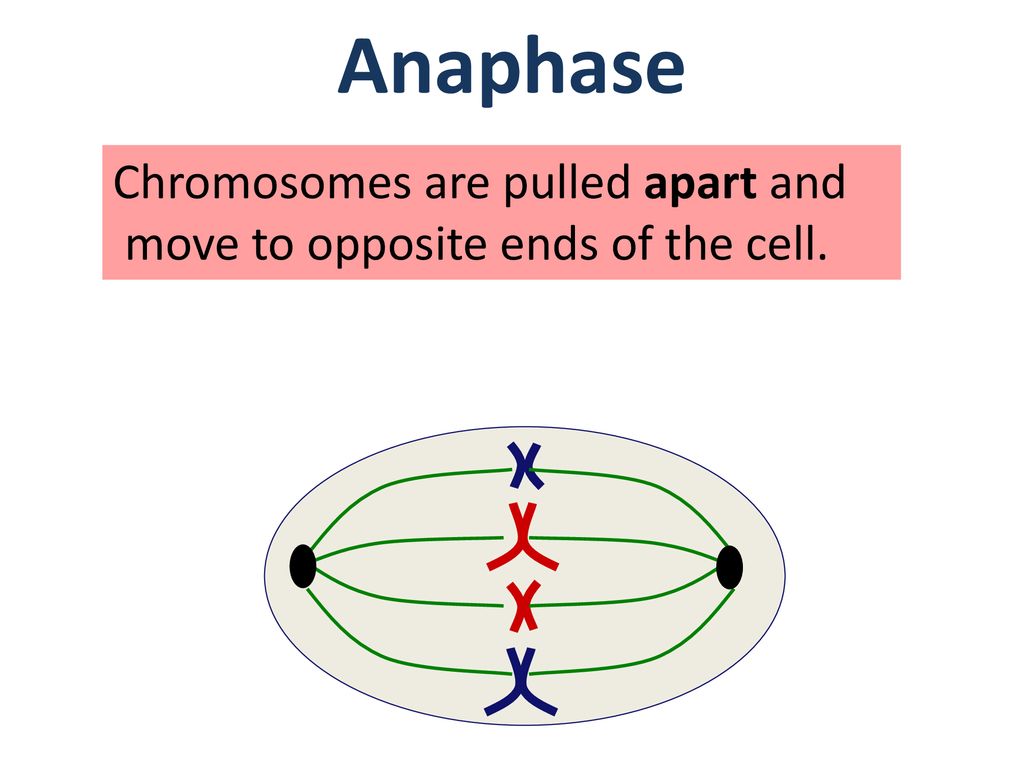
Anaphase Definition. Anaphase is a stage during eukaryotic cell division in which the chromosomes are segregated to opposite poles of the cell. The stage before anaphase, metaphase, the chromosomes are pulled to the metaphase plate, in the middle of the cell.Although the chromosomes were heavily condensed in the start of cell division, they continue to condense through anaphase.

Anaphase, in mitosis and meiosis, the stage of cell division in which separated chromatids (or homologous [like] chromosome pairs, as in the first meiotic division) move toward the opposite poles of the spindle apparatus. Anaphase is preceded by metaphase, in which the chromosomes line up along the The polar movement of the chromosomes or
Mechanisms of chromosome behaviour during mitosis Biology Diagrams
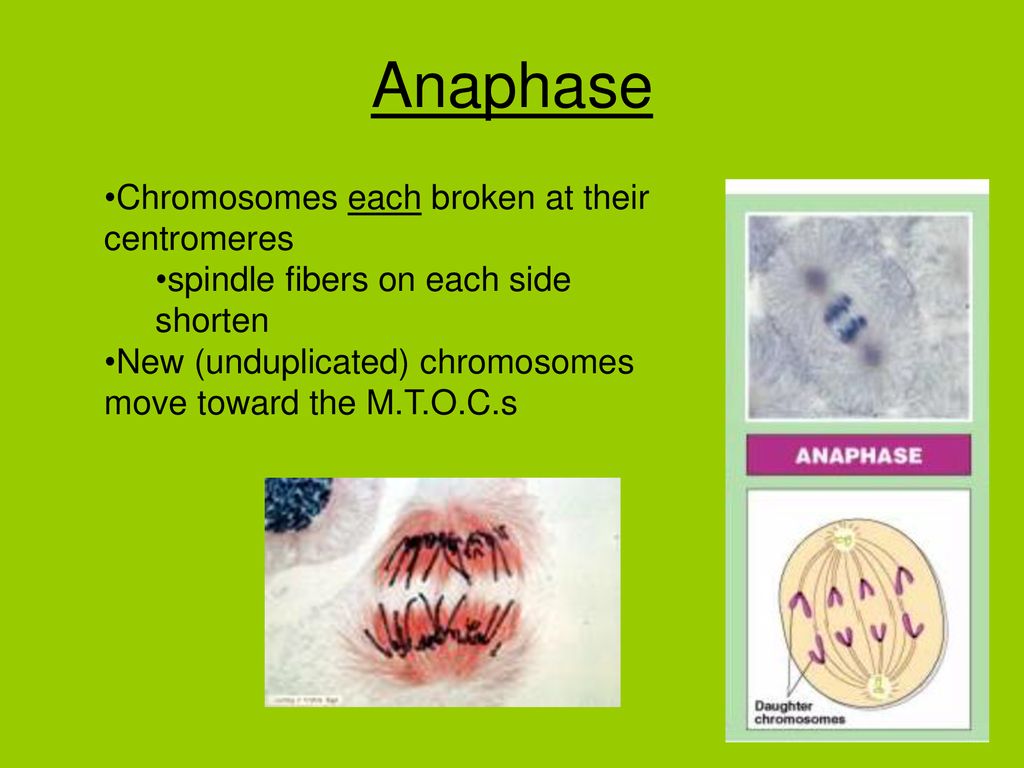
Introduction to Chromosome Movement: Chromosomes are involved in a series of directed movements during both mitosis and meiosis. With the separation of the sister chromatids/homologues at anaphase, the equilibrium is broken, the chromosomes move towards the poles at the rate of about 1 pm/min.

Anaphase I is the third stage of meiosis I and follows prophase I and metaphase I. This stage is characterized by the movement of chromosomes to both poles of a meiotic cell via a microtubule network known as the spindle apparatus. The Xenopus chromokinesin Xkid is essential for metaphase chromosome alignment and must be degraded to allow anaphase chromosome movement. Cell 102, 411-424 (2000).

